When releasing a custom library, it can be tedious to manually build it locally, upload it to TestPyPI for verification, then upload it to PyPI, and finally tag and release it…
So, I decided to automate the deployment using GitHub Actions.
Objective of This Article
When you push a tag to the remote repository, this setup will automatically upload your package to PyPI and create a GitHub release.
After you push a tag from your local environment…
git tag vX.X.X
git push origin vX.X.XThe following steps will be automatically executed in order:
- Upload to TestPyPI
- Upload to PyPI
- Create a release on GitHub and distribute the source code
We will create a workflow as shown in the image below.
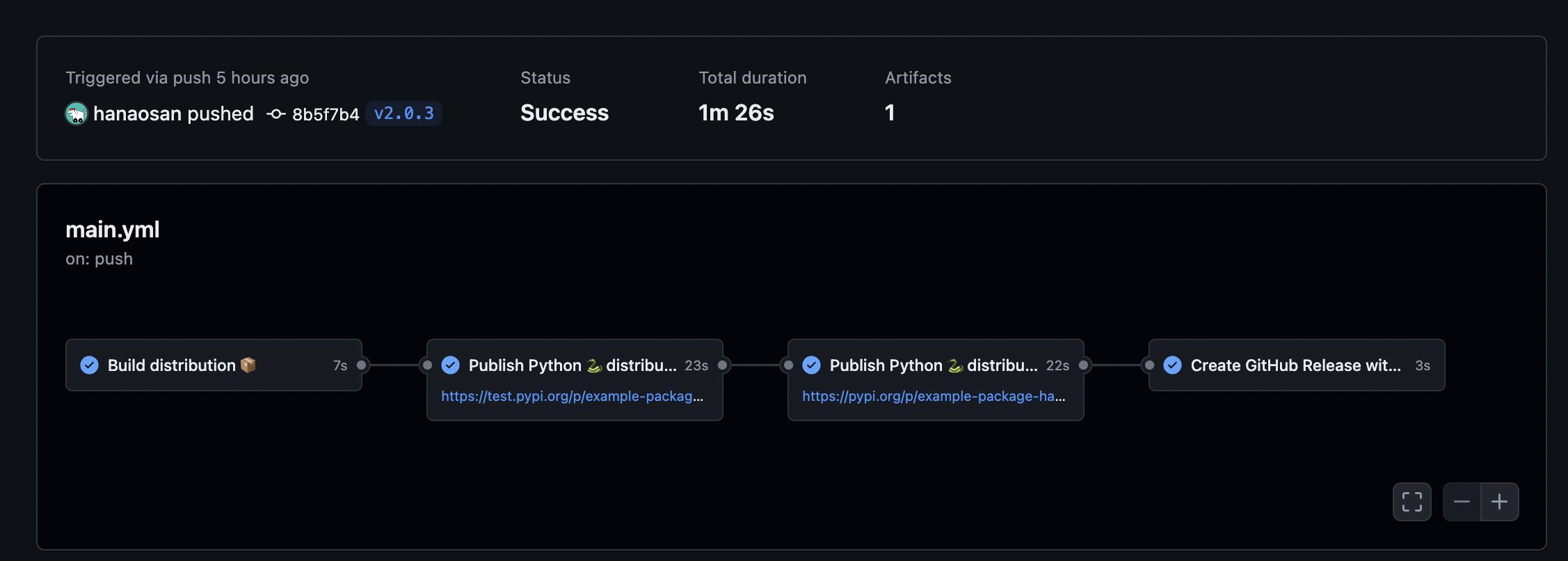
Steps
Preparation
Note: Instead of using setup.py as the packaging tool configuration file, we will use pyproject.toml. According to PEP-518, pyproject.toml is recommended for modern Python projects.
Prepare your Python package and upload it as a project to both PyPI and TestPyPI.
If you already have a custom library on PyPI, you can skip this step.
Follow the tutorial below to upload a sample package to TestPyPI and PyPI:
Creating a Workflow File in GitHub Actions
In your repository, go to Actions > Set up a workflow yourself > Create a YAML file with any name (in this case, main.yaml) and commit it.
It’s okay if the file is empty initially.
Setting Up Publishing in PyPI
Traditionally, to upload a package from GitHub Actions to PyPI, you would need to create an API token in PyPI and store that token as a secret in GitHub.
However, by using Publishing, you can automatically issue and authenticate a temporary token when connecting to pre-configured services (including specific users, repositories, etc.)!
Publishing is easier to set up, and since the token has a short expiration time, it also offers better security.
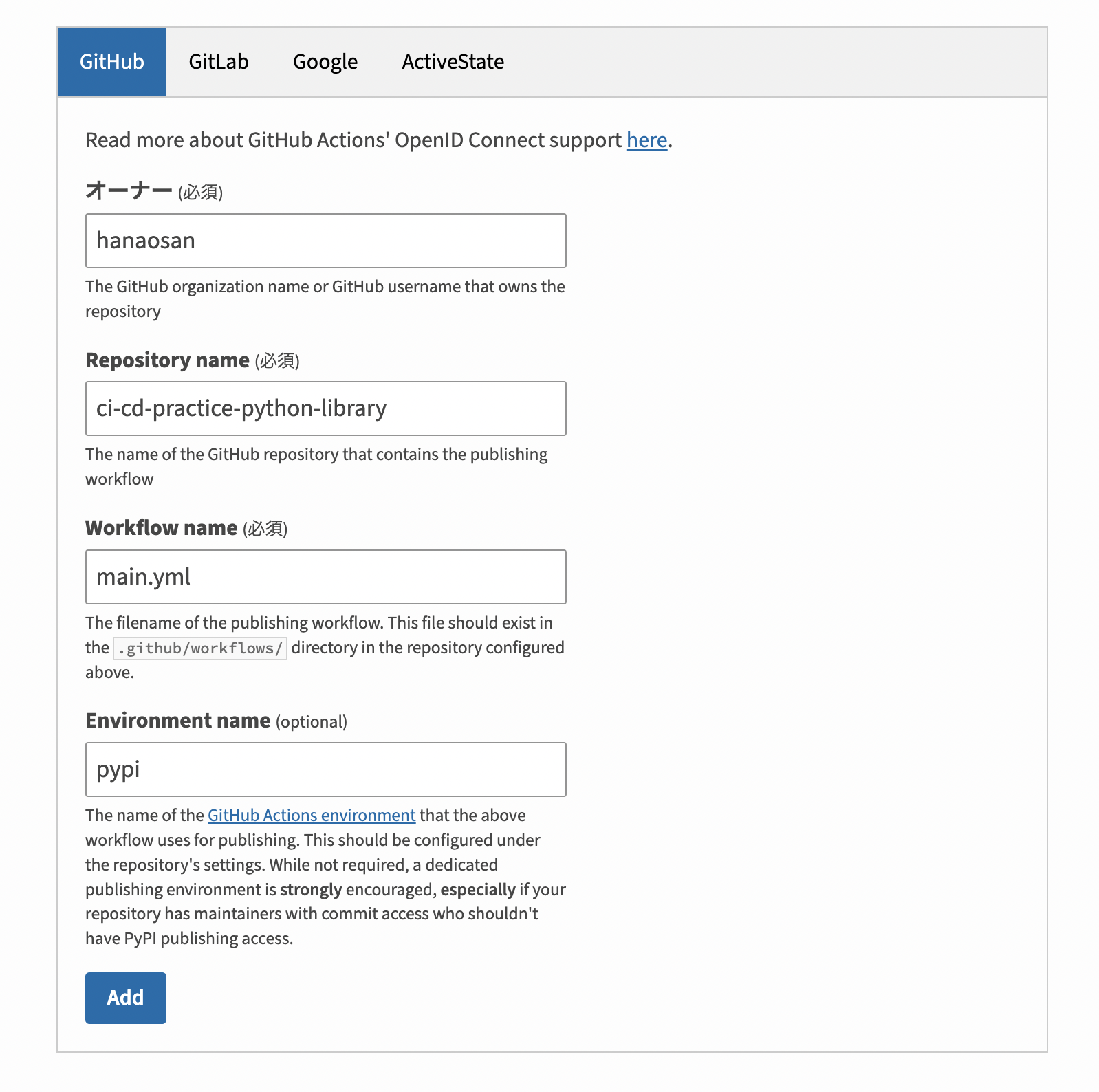
From your project page on PyPI, select Publishing > Add a new publisher.
Fill in the fields as shown in the image below and click Add.
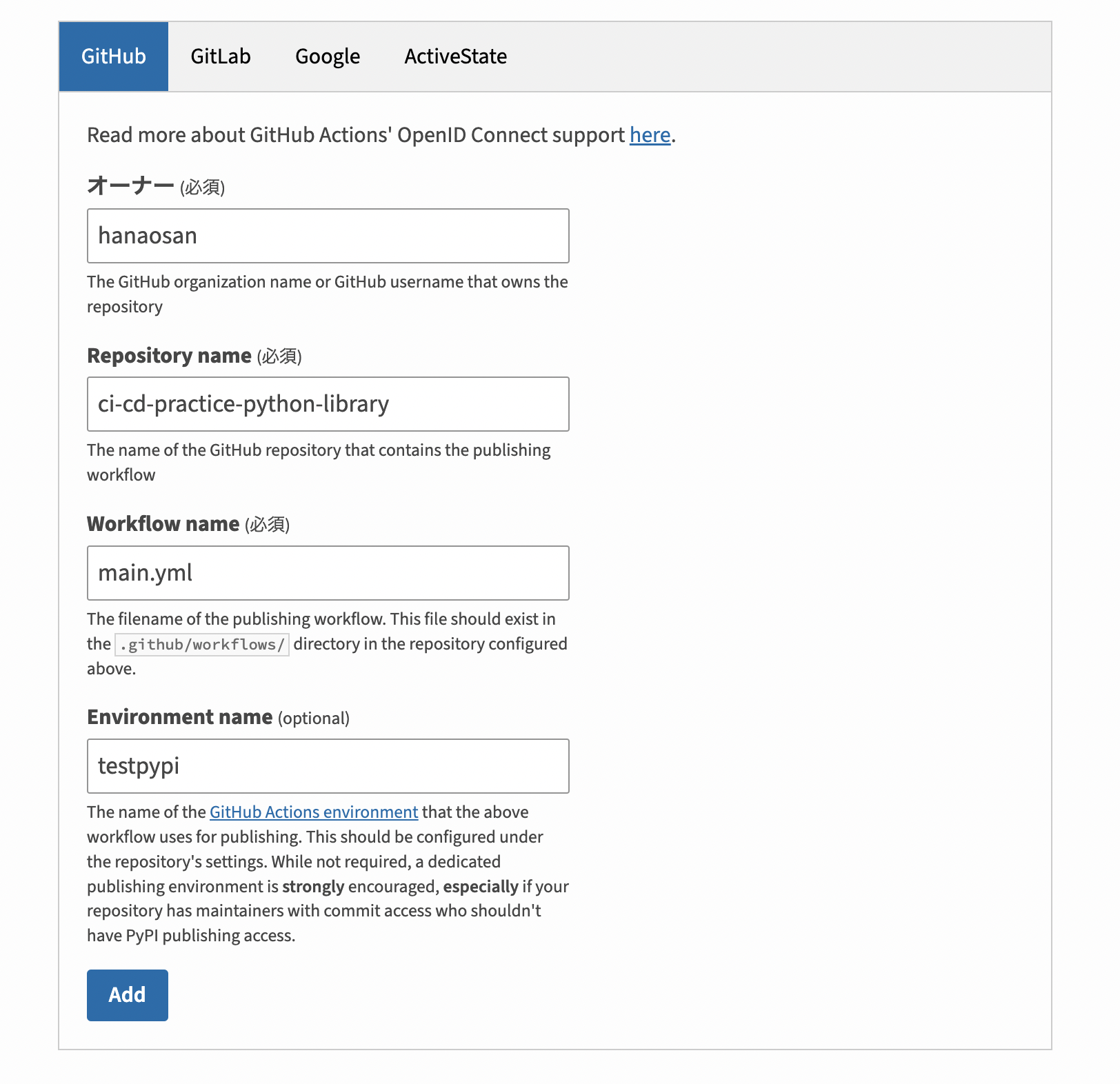
Next, open TestPyPI and create a publisher in the same way.
Use a different environment name than the one used for PyPI.
Workflow in GitHub Actions
Now let’s write the workflow in the YAML file you just created.
1. Start the Workflow When a Tag is Pushed
name: Publish Python 🐍 distribution 📦 to PyPI and TestPyPI
on:
push:
tags:
- 'v*.*.*'2. Build
To build the package, pyproject.toml must exist in the repository, so make sure it is not included in .gitignore.
jobs:
build:
name: Build distribution 📦
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4 # Checkout the code
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5 # Set up the Python environment
with:
python-version: "3.x"
- name: Install pypa/build # Install the build tool
run: >-
python3 -m
pip install
build
--user
- name: Build a binary wheel and a source tarball
run: python3 -m build # Build the package
- name: Store the distribution packages # Temporarily store the build artifacts in the dist directory under the name python-package-distributions
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: python-package-distributions
path: dist/3. Publish to TestPyPI
publish-to-testpypi:
name: Publish Python 🐍 distribution 📦 to TestPyPI
needs:
- build # Start the job only if the build job has completed
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
environment:
name: testpypi # Enter the environment name set in the Publisher
url: https://test.pypi.org/p/example-package-hanaosan0318 # Project URL
permissions:
id-token: write # Grant Publishing permissions
steps:
- name: Download all the dists # Download the build artifacts that were saved earlier
uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
with:
name: python-package-distributions
path: dist/
- name: Publish distribution 📦 to TestPyPI # Publish to TestPyPI
uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v1
with:
repository-url: https://test.pypi.org/legacy/4. Publish to PyPI
publish-to-pypi:
name: >-
Publish Python 🐍 distribution 📦 to PyPI
needs:
- publish-to-testpypi # Start the job only if the TestPyPI publishing job has completed
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
environment:
name: pypi # Enter the environment name set in the Publisher
url: https://pypi.org/p/example-package-hanaosan0318 # Project URL
permissions:
id-token: write
steps:
- name: Download all the dists
uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
with:
name: python-package-distributions
path: dist/
- name: Publish distribution 📦 to PyPI
uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v15. Create a GitHub Release
github-release:
name: >-
Create GitHub Release with source code
needs:
- publish-to-pypi # Start the job only if the PyPI publishing job has completed
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: write # Grant permission to create a GitHub release
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4 # Checkout the code
- name: Create GitHub Release
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} # A temporary token that is automatically generated each time the workflow is run
run: >-
gh release create
'${{ github.ref_name }}'
--repo '${{ github.repository }}'
--notes "Release for version ${{ github.ref_name }}"Finally, you have defined the workflow!
You can view the entire YAML file at the following link:
Deploying
Update the version in pyproject.toml to the release version and push the changes.
[project]
name = "example_package_hanaosan0318"
version = "2.0.3" # Change to the release version
authors = [
{ name="Example Author", email="author@example.com" },
]Create a tag and push it.
git tag v2.0.3
git push origin v2.0.3The package will be uploaded to PyPI and TestPyPI.
A release will also be created, and you can see the source code distributed in zip and tar.gz formats.
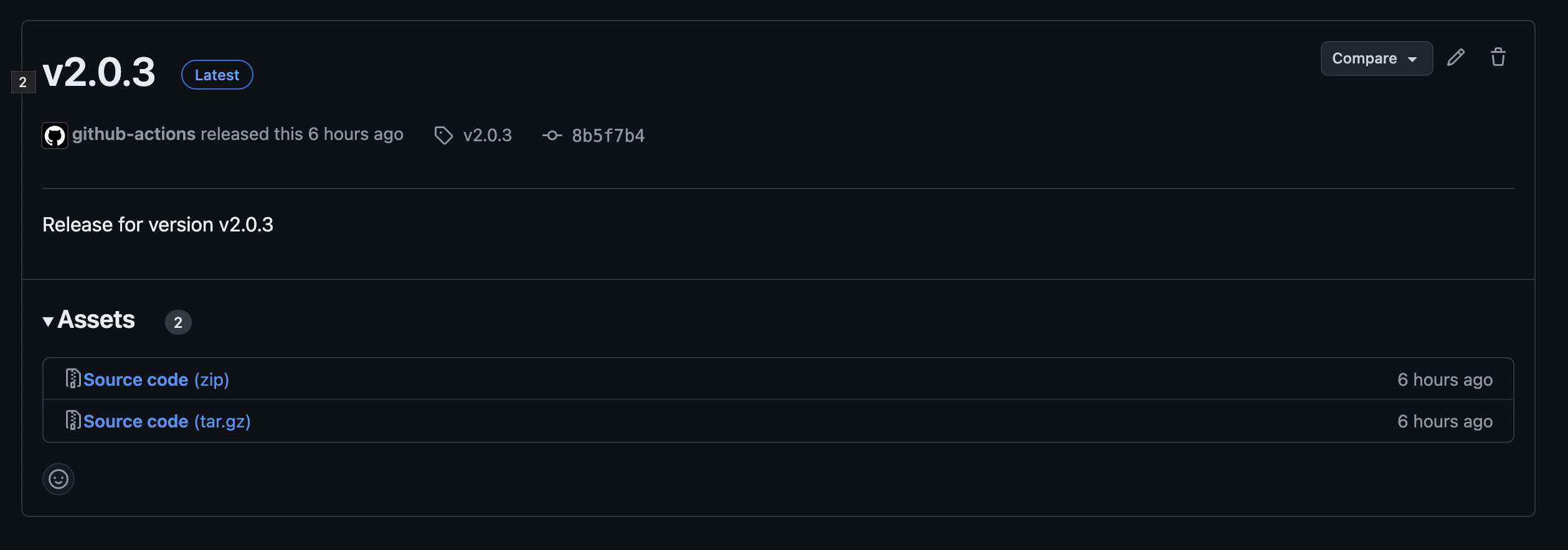
And that’s it!
You have now automated the process of uploading your package to PyPI and creating a release on GitHub when you push a tag to the remote repository.
References
- Repository: https://github.com/hanaosan/ci-cd-practice-python-library
- Publishing package distribution releases using GitHub Actions CI/CD workflows

Leave a Reply